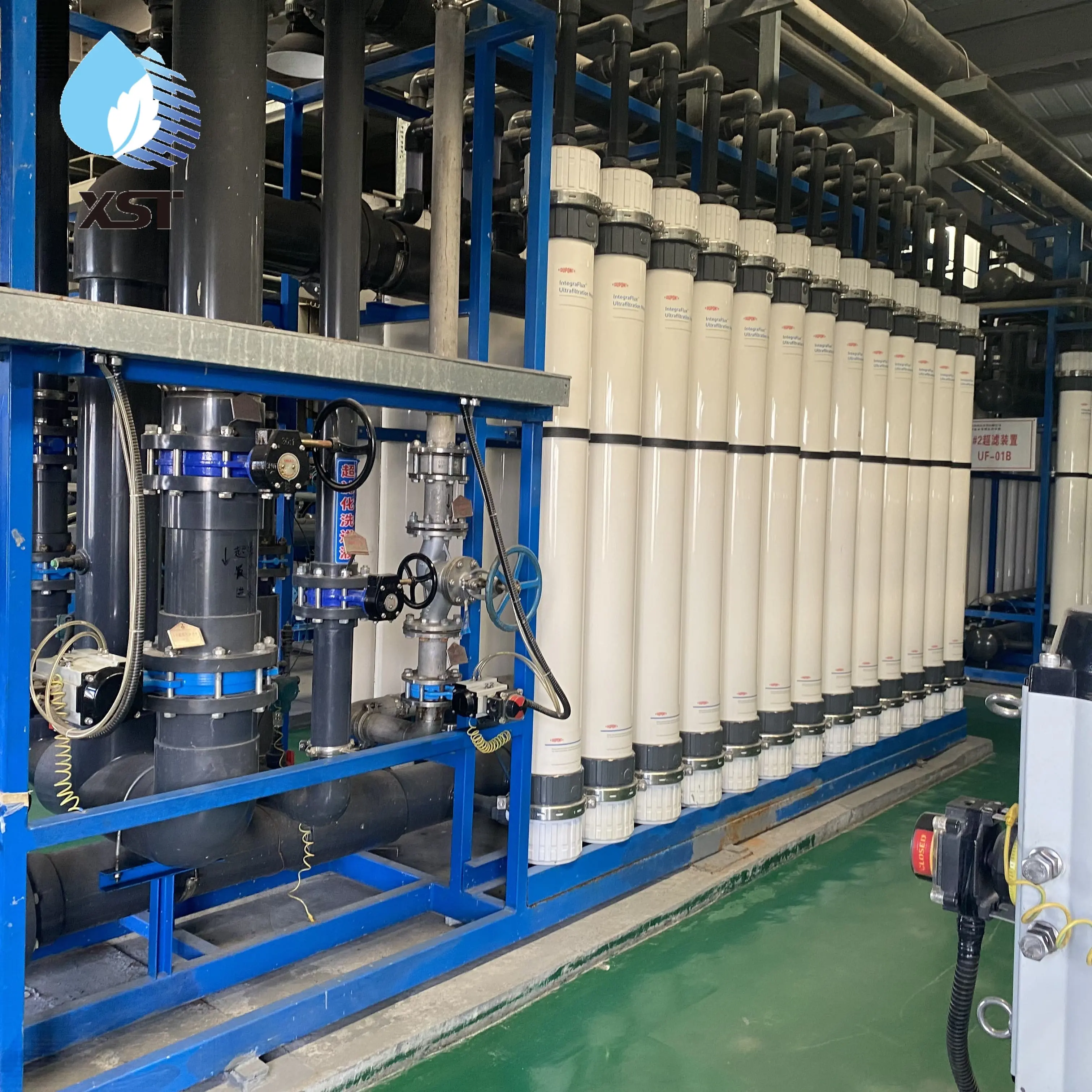
Multifunctional application of activated carbon in membrane water treatment
Activated carbon plays a key role in drinking water purification, industrial wasteWater Treatment and other fields due to its unique physical and chemical properties. Its core functions include:
Adsorption and removal of pollutants: Activated carbon has a specific surface area of 500-1500m²/g and an average micropore diameter of 2-3nm. It can adsorb 60%-80% of colloidal substances, 47%-60% of organic matter (such as humic acid, lignin sulfonic acid) and 50% of iron ions in water. For example, after a chemical plant used activated carbon for filtration, the effluent COD (chemical oxygen demand) dropped from 120mg/L to 50mg/L, a decrease of 58%.
Chemical oxidation and dechlorination: The surface of activated carbon is rich in functional groups such as hydroxyl and carboxyl, which can decompose free chlorine through chemical adsorption and catalysis. Experimental data show that its removal rate of residual chlorine exceeds 95%. During the reaction, chlorine (Cl₂) is hydrolyzed to generate hypochlorous acid (HClO), which is further decomposed into hydrochloric acid (HCl) and new ecological oxygen ([O]) under the catalysis of activated carbon. The latter reacts with carbon to generate carbon dioxide and is discharged from the system. The reaction formula is:
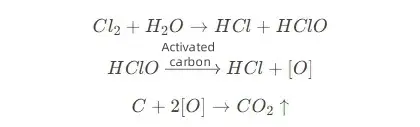
Protecting ion exchange resin: In the desalted water process, the Activated Carbon Filter is often placed before the cation exchanger, which can intercept more than 90% of free chlorine and 60% of organic matter, avoiding resin oxidation failure and organic contamination of strong alkaline resin.

















