01
Electrodeionization (EDI) Water System
products Video
products description
EDI technology substitutes the traditional hybrid ion exchange demineralization process (DI) with an electroregenerative ion exchange demineralization process. High desalination efficiency is achieved through the combined action of ion exchange resin and selective ion membranes, complemented by reverse osmosis to produce water of ultra-high quality, reaching resistivity levels of 10~15MΩ·CM.

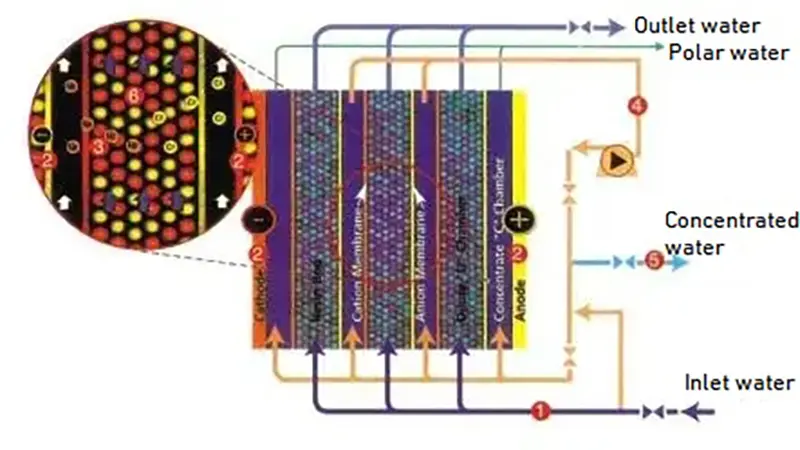

How EDI High-Purity Water Equipment Works
1. Electrodialysis: Under the influence of a direct current electric field, ions in water migrate toward oppositely charged electrodes and are separated by selective ion exchange membranes.
2. Ion Exchange: The EDI module is filled with ion exchange resin, which absorbs ions from water and further removes impurities.
3. Regeneration: The ion exchange resin within the EDI module undergoes continuous regeneration under the electric field, eliminating the need for chemical regenerants and enabling continuous operation.
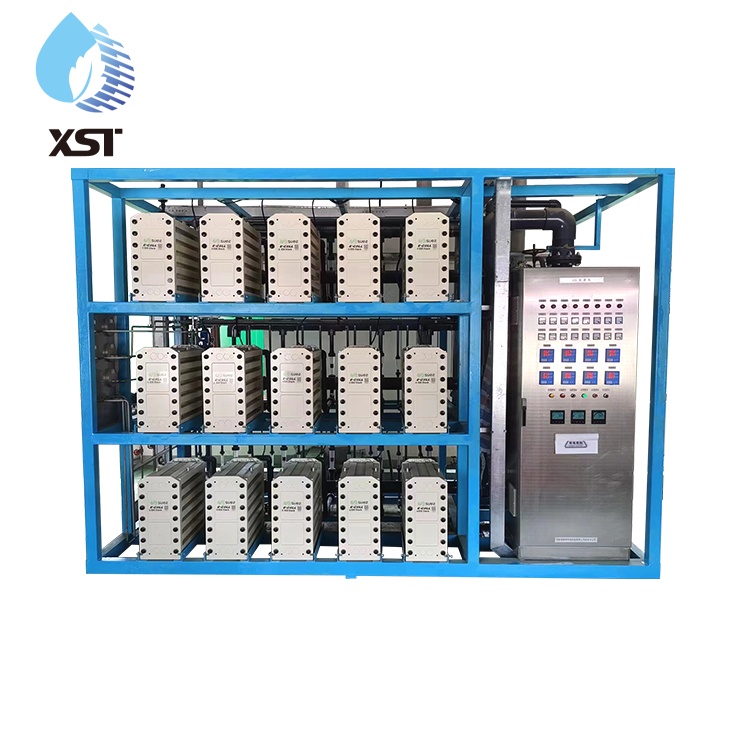
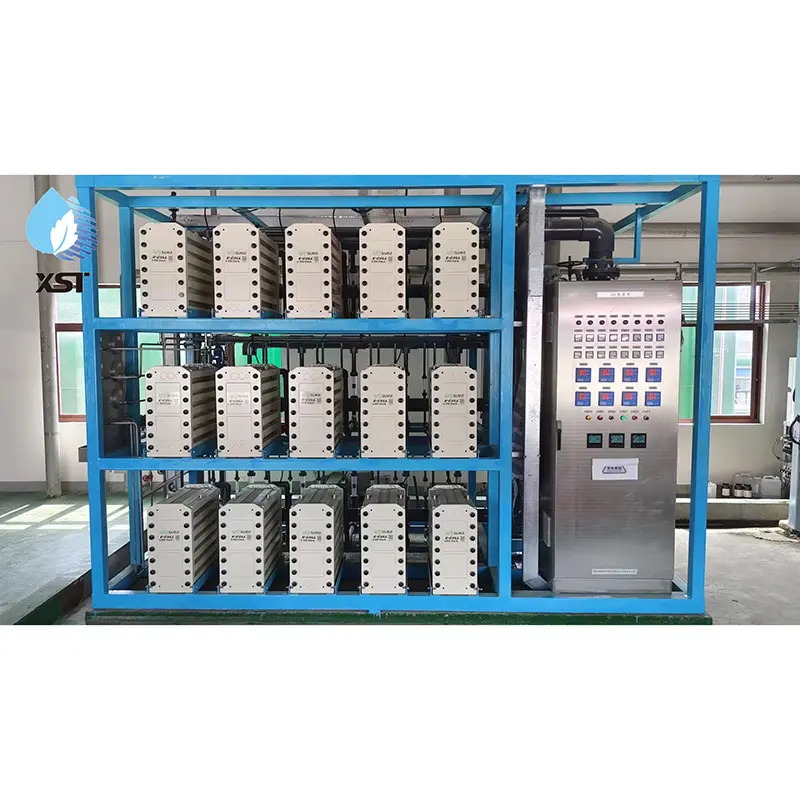
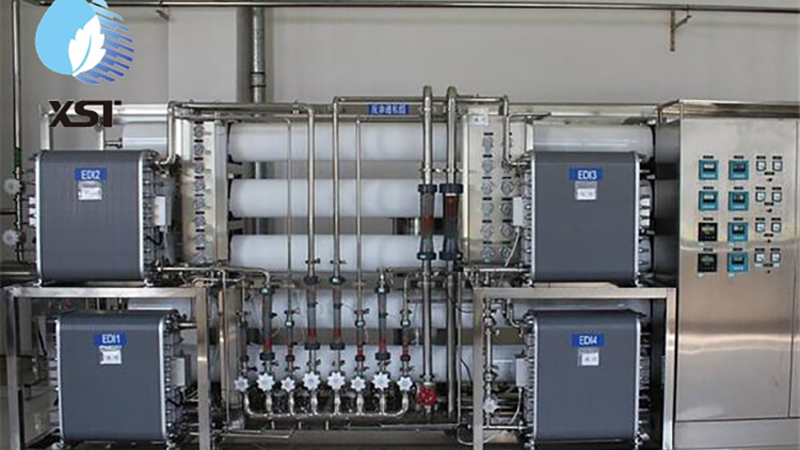
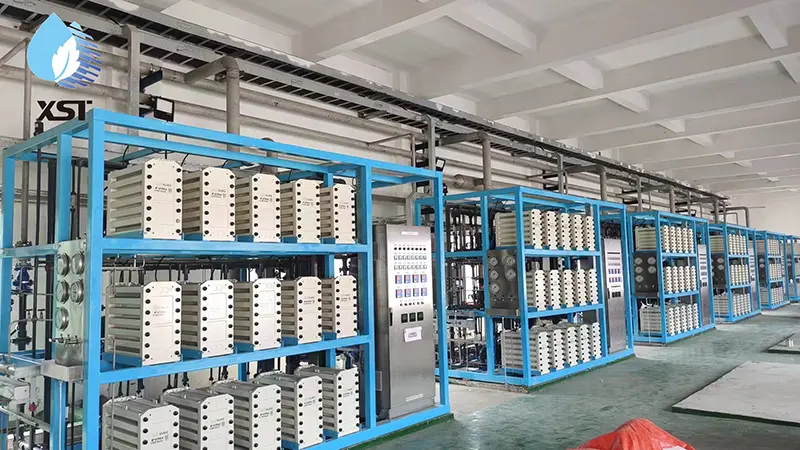
Composition of EDI High-Purity Water Equipment
1. Pre-treatment System: Includes multi-media filters, activated carbon filters, softeners, etc., designed to remove suspended particles, organic matter, and hardness ions from water.
2. Reverse Osmosis System (RO): Acts as pre-treatment for EDI, removing most ions and organic matter from water.
3. EDI Module: The core component that utilizes electrodialysis and ion exchange technology to remove trace ions from water.
4. Post-treatment System: Incorporates UV sterilizers and precision filters to ensure the final water quality meets stringent purity standards.
Conditions of Use
| Water Source | RO water production, conductivity 1-20μs/cm, maximum conductivity ≤30μs/cm (NaCl) |
| Inlet Hardness | < 1.0ppm (CaCO3) (recommended below 0.5ppm) |
| Total CO2 | < 3ppm |
| pH Value | 7.5-9 |
| Influent Organic Matter | TOC < 0.5ppm |
| Influent Oxidizer | Cl2 (active) < 0.03ppm, O3 (ozone) < 0.02ppm |
| Influent Heavy Metal Ions | Fe, Mn, variable valence metal ions < 0.01ppm |
| Inlet Silicon | SiO2 < 0.5ppm |
| Inlet Water Particle Size | < 1μm |
| Temperature | 15℃--35℃ |
| Inlet Pressure (DIN) | 0.15-0.4MPa |
| Concentrated Water Inlet Pressure (CIN) | 0.10-0.3MPa |
| Water Production Pressure (DOUT) | 0.05-0.25MPa |
| Concentrated Water Outlet Pressure (COUT) | 0.02-0.2MPa |
Application Fields
1. Electronics Industry: For the preparation of ultra-pure water in semiconductor and integrated circuit production processes.
2. Power Industry: Used for boiler feedwater, cooling water, and other applications.
3. Pharmaceutical Industry: For injection water, cleaning water, and similar uses.
4. Chemical Industry: For the production of high-purity chemicals.
The EDI device is typically placed after an electrodialyzer or reverse osmosis system (or directly applied to low-salt-content water), replacing ion exchangers to achieve further desalination and produce higher-purity water. It finds widespread application in electronics, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, atomic energy, and power industries.




















